Last updated: 2025-08-29
Vehicle types (window)
In this article
Register > Vehicle types
In this window, you make settings for the vehicle types you are dispatching. This has an impact on route optimisation and how shipments are carried out, among other things.
For instructions, see Adding a new vehicle type.
The vehicle types can, but do not have to, match the price vehicle types in the Price vehicle types registry.
Difference between vehicle type and price vehicle type
The price vehicle type forms the price basis. It is applied to the order and can be selected by the customer in the customer portal, for example. The vehicle type is used in dispatch and affects how the transport is carried out. It is basically the same, but there is a registry for each of them, so it is possible to make different settings depending on how you want to handle vehicle types that form the basis for prices and planning..
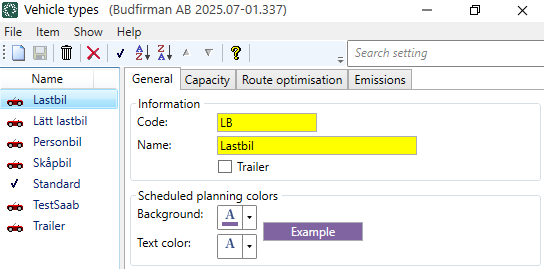
General
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Code |
Used for identification in dispatch. |
|
Name |
Used for identification. The name is shown in the list on the left when a new configuration is saved. |
|
If you specify that the vehicle type is a trailer, you should fill in your own values on the Route optimisation tab, as PTV does not have a vehicle profile only for trailers. It is not possible to route optimise trailers on their own; it is instead the vehicle pulling the trailer that is route optimised. |
|
|
Background Text color |
The vehicle type cannot be displayed in the shipment lists in dispatch, as only the price vehicle type and vehicle can be displayed there. These colours only apply to the Schedule planning tab in dispatch. Select colours and type something in the text field on the right to see how it will look. |
Route optimisation
Dimensions for PTV
These values are used for route optimisation.
-
If you do not select a vehicle profile and do not fill in any fields, "truck-40t" from PTV is used.
-
If you select a vehicle profile and manually enter a value in any of the fields, that value applies instead of the default value from PTV.
-
If the fields are left blank, PTV’s default values are used instead.
Optimising a route for larger or heavier vehicles than the profile that has been selected may result in the vehicle not actually being able to take the route calculated if, for example, there are weight restrictions on the roads or viaducts that the vehicle cannot pass under. Always check the PTV values for the vehicle profile in the corresponding XML file at https://xserver2-dashboard.cloud.ptvgroup.com/dashboard/Default.htm#Administration/FileViewer.htm.
Even if you want to use the default profile "truck-40t", it may be a good idea to select it in the drop-down list, otherwise it will be unclear which vehicle profile applies.
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Vehicle profile |
Ready-made profiles from PTV with default values for the dimensions. If a profile is not selected, "truck-40t" is used. The specifications of the PTV vehicle profiles are available in the PTV xServer help. To create a customised vehicle profile, enter a name and fill in values for the dimensions. However, the profile cannot be reused on other vehicle types. The field can also be left blank and just the values filled in. |
|
Emission class, Euro |
The emission class is not taken from the PTV vehicle profile. An emission class must be selected actively here if you want to change the default setting. [Default] = Euro 5. If you enter both Emission class, Euro and Emission class, CO2 (EU) (drop-down list below), the following EU Directives apply If you enter Euro 6, Euro 7 or Euro EEV, you must enter Emission class, CO2 (EU) 2, 3 or 4. |
|
Emission class, CO2 (EU) |
The CO2 emission class is an EU requirement. The emission class is not taken from the PTV vehicle profile. An emission class must be selected actively here if you want to change the default setting. [Default] = 1.
|
|
Total weight (kg) |
truck-40t (default): 40,000 |
|
Max. axle pressure (kg) |
truck-40t (default): 10,000 |
|
Number of axles |
truck-40t (default): 5 |
|
Height (cm) |
truck-40t (default): – |
|
Length (cm) |
truck-40t (default): 1,875 |
|
Width (cm) |
truck-40t (default): – |
|
Cylinder volume (ccm) |
truck-40t (default): – |
|
Height above front axle (cm) |
truck-40t (default): – |
|
Here you can choose whether the route optimisation should take into account the road bearing capacity class, and if so, which bearing capacity classes should be used in the first place. Roads with the classifications that are not selected will be penalised with the value you set for Bonus value.
More information on the classifications is available on the PTV website. There are more bearing classes than those listed here, but they cannot be selected in Opter. Database fields: VHT_PreferredRoutes |
|
|
Bonus value |
Enter a value between 0 and -100. The value indicates how much less weight is given to roads that do not have the bearing capacity classes you specified above. |
|
Particle filter installed |
truck-40t (default): – |
|
Take limitations, such as vehicle heights at viaducts and vehicle weights at bridges, into account when calculating distances. Recommended for trucks and other large vehicles. May lead to longer calculation times. |
|
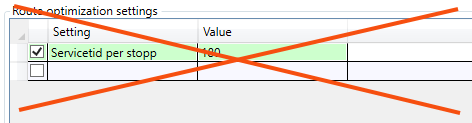
Route optimisation settings
It is only for internal Opter use, and should not be used. Even if a row is added and a value is entered in the table, such as "Service time per stop 180 seconds", it is not used in the route optimisation.
Emissions
In this tab you make settings so that Opter can calculate CO2 emissions. For more information, see CO2 emissions in grams, overview, Settings for CO2 emission calculations (and CO2 emissions in tonnes).
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CO2 emissions (g/km) |
CO2 emissions of the vehicle type in grams per km. If you enter Fuel, Fuel consumption (per 100 km) and CO2 emissions (g/km), Opter will use the value in the CO2 emissions (g/km) field to calculate CO2 emissions for shipments and orders. If you want Opter to calculate the CO2 emissions of the vehicle type itself (in g/km), leave the field CO2 emissions (g/km) empty and fill in the fields Fuel and Fuel consumption (per 100 km). The data on CO2 emissions is taken firstly from the vehicle, secondly from the vehicle type and thirdly from the price vehicle type. If the shipment is subcontracted, the CO2 emissions data will be obtained firstly from the subcontractor and secondly from the price vehicle type. For more information, see Settings for CO2 emission calculations. |
|
Fuel |
Vehicle type’s fuel. The CO2 emissions of the fuel must be entered in the fuel register. For more information, see Settings for CO2 emission calculations. |
|
Fuel consumption (per 100 km) |
Average fuel consumption of the vehicle type in the selected unit per 100 km. The unit is set in the fuel registry. Example: 0.8 litres per mile = 8 litres/100 km. If you enter Fuel, Fuel consumption (per 100 km) and CO2 emissions (g/km), Opter will use the value in the CO2 emissions (g/km) field to calculate CO2 emissions for shipments and orders. If you want Opter to calculate the CO2 emissions of the vehicle type itself (in g/km), leave the field CO2 emissions (g/km) empty and fill in the fields Fuel and Fuel consumption (per 100 km). The data on CO2 emissions is taken firstly from the vehicle, secondly from the vehicle type and thirdly from the price vehicle type. If the shipment is subcontracted, the CO2 emissions data will be obtained firstly from the subcontractor and secondly from the price vehicle type. For more information, see Settings for CO2 emission calculations. |
|
Capacity converted into pricing weight (kg) |
This field is used if you want to take into account the pricing weight of the order compared to the capacity of the vehicle type. For more information, see Settings for CO2 emission calculations. |