Last updated: 2017-01-01
Account coding for commission
In this article
Here are examples of how you can post commissions in Opter. The new account is taken primarily from the Account field in Resource Pricing Settings and secondarily from the Account for commission field in VAT rates. Hereinafter referred to as “New Account”.
Normal account coding
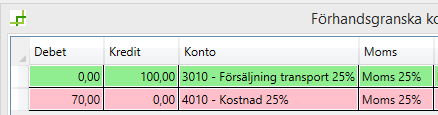
Commission is recorded as sales to customer (other account)
When you account for commission as if it were a sale to a customer, it means that the sale is moved from one sales account to another, without VAT being affected.
-
The existing sales account is credited (reduced) by the commission amount.
-
“New account” (sale) is debited (increased) by the commission amount.
-
VAT is not affected.
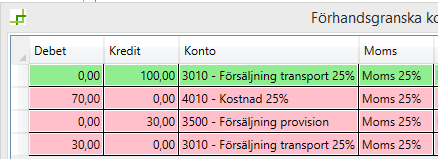
Commission is recorded as sales to the haulier
The entire price paid by the customer is recognised as an expense. The commission is then added to the price. It can be considered to be like having a gross turnover consisting of a price and a commission and a net turnover consisting of a price. This approach is suitable if the haulier wants to see the full price as revenue on his supplier bill and treat the commission as an expense. One reason for doing so may be that the trader must account for VAT on income and expenses separately, and cannot offset them against each other.
-
The existing cost account is debited (increased) by the commission amount (to match the customer price).
-
“New account” (sale) is credited (increased) by the commission amount.
-
Input VAT is charged (added) to match the increased sales.
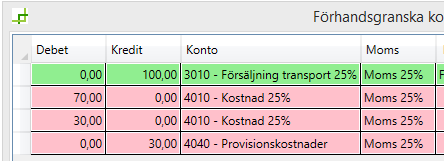
Commission is recognised as a cost to the haulier
Increase the cost to match the customer price and then offset the increased cost against another cost account.
-
The existing cost is debited (increased) by the commission amount (to match the customer price).
-
“New account” (cost) is credited (increased) by the commission amount.
-
VAT is not affected.